As announced at Budget 2021, the government is consulting on the implementation of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Model Reporting Rules for Digital Platforms, which require digital platforms to report details of the income of sellers on their platform to the tax authority and also to the sellers.
Consultation description
Following the announcement at Spring Budget 2021, the government is consulting on the implementation of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development’s (OECD’s) Model Reporting Rules for Digital Platforms. From January 2023, these rules will require platforms to report information about the income of sellers providing goods and services to help sellers get their tax right and to enable HMRC to detect and tackle non-compliance.
The consultation sets out the details of the rules and seeks views on the government’s implementation, including on optional elements of the rules. The government welcomes input from a wide range of stakeholders to ensure the rules are implemented proportionately and effectively.
Foreword
The digital economy empowers individuals and businesses to connect with consumers both at home and abroad. It thereby offers huge benefits and opportunities for UK businesses, workers, and consumers, which is why the government is committed to encouraging the growth of the UK’s digital economy.
However, the growth of the digital economy also creates challenges of compliance and tax collection for HM Revenue & Customs (HMR”) and other tax authorities. To address some of these challenges the OECD has developed model rules for digital platforms to report the income of individuals or companies selling goods or providing services via their platform (“sellers”) to the tax authority where the platform is resident, incorporated or managed. This information will then be sent to the tax authority where the seller is resident. The platforms will also be required to provide a copy of the information to the seller, which will help the seller declare the correct amounts for tax purposes.
The UK plays a leading role in promoting international tax cooperation and transparency, and the UK government contributed to the development of the OECD model rules. At Spring Budget this year, the Chancellor of the Exchequer announced that the government will consult on the implementation of the rules and this announcement has been widely welcomed.
The new rules will improve international cooperation on the exchange of information for tax purposes. They will allow HMRC to have access to data from platforms based outside the UK quickly and efficiently, which should encourage compliance and increase the visibility of transactions. The rules will also help taxpayers to get their tax right, and will help HMRC to detect and tackle tax non-compliance. The fact that the rules are standardised is designed to ensure that platforms do not face a patchwork of different tax reporting requirements across jurisdictions, minimising the administrative burdens on them.
The government is aware of the need for proportionate and measured reform, especially given the present recovery from COVID-19. The reporting rules for digital platforms will come into force from January 2023 at the earliest. This will give a long lead-in time for platforms to prepare for the new rules.
I would encourage the widest possible range of stakeholders to give their views through this consultation process. The government welcomes feedback from digital platforms large and small, gig workers and small businesses operating on platforms, and representative bodies, so that it can ensure that the implementation of the OECD reporting rules for digital platforms is balanced and effective.
Rt. Hon. Jesse Norman, Financial Secretary to the Treasury
1. Introduction
Background to the OECD model rules
1.1 The use of digital platforms, which are websites or apps that facilitate transactions between providers of goods and services (sellers) and their customers, is growing rapidly. This provides the opportunity for sellers to work more flexibly and more easily access customers globally at a lower cost. As a result, there are increasing numbers of people who will need to declare their income from online transactions and complete their own income tax return.
1.2 In some cases, sellers of goods and services may not get their tax right. This could be for a variety of reasons including failing to understand their tax obligations, not keeping track of income across multiple different platforms, or a conscious decision not to tell the tax authorities about their taxable income. The flexibility of the opportunities created by platforms also leads to complexity in sellers’ tax affairs. As a result, some sellers may under declare their taxable income or not declare it at all.
1.3 Growing digital platform activity presents opportunities for tax authorities to have greater visibility over sellers’ income and support them to be tax compliant, as transactions are recorded electronically. This enables information sharing with tax authorities, as well as enabling sellers to access a record of their transactions and income, making it easier to get their tax right.
1.4 Tax administrations may gain visibility over the income of sellers through requiring digital platforms to report this information, with carve-outs for those who present a low compliance risk. However, as platforms are based overseas, there is limited effectiveness in tax authorities operating individually to implement domestic reporting agreements, given the challenges of enforcing such reporting on companies overseas. This is an issue replicated across multiple jurisdictions. Such a fragmented approach would also be burdensome and inefficient for digital platforms, who would have to comply with multiple different reporting regimes.
1.5 The OECD therefore developed Model Reporting Rules with respect to the provision of services (“model rules”) in consultation with the UK and other member jurisdictions to provide a standardised way of collecting and reporting relevant information about sellers and their income from digital platform activities to tax authorities. This approach enables jurisdictions to effectively enforce the reporting regime on an international level and facilitates the exchange of information between such jurisdictions. It also means platforms operating in multiple jurisdictions avoid facing a number of different domestic reporting requirements.
1.6 The OECD published the model rules in June 2020. Jurisdictions can opt into implementing the model rules with the UK being one of the first countries to confirm that it would do so. Subsequently, the OECD has included an optional module in the model rules to extend their scope to the sale of goods and transport rental, and published the resulting changes to the rules in June 2021.
How the model rules work
1.7 Broadly, the OECD model rules work as follows:
- platforms must collect certain details about their sellers, including information to accurately identify who the seller is and where they are based, as well as how much they have earned on the platform over an annual period
- platforms must verify the seller’s information to ensure it is accurate
- platforms must report the information, including the seller’s income, to the tax authority annually by 31 January
- platforms must also give that information to the sellers, so that they can use it to help them complete their tax returns
- tax authorities then exchange information with other tax authorities where the sellers are resident (or rental property is located)
- the information is used by tax authorities to ensure that sellers are complying with their tax obligations and to tackle non-compliance if they are not
- tax authorities must enforce the rules and see that platforms are operating them correctly, and there may be penalties for non-compliance
UK policy objectives in implementing the model rules
Making it easier for sellers to get their tax right
1.8 The government is committed to making it easier for taxpayers to get their tax right first time. Requiring platforms to provide information to sellers about the income they have earned on the platform will support this policy objective. This will raise sellers’ awareness of their tax obligations, and support them to fill in their tax returns or check the information they have filed with the tax authority is correct. The government is also considering how platforms can work with HMRC to build on the work they already do to support their sellers to be tax compliant, for example, by providing links to relevant HMRC guidance.
Identifying and tackling tax evasion and non-compliance
1.9 The government wants to bear down on tax evasion, particularly involving platforms located in other jurisdictions. Implementing the OECD rules will allow the exchange of seller information with other tax authorities which will give HMRC quick, efficient and secure access to data on UK resident sellers and rental property in the UK from platforms based outside the UK. This will ensure that taxable activities do not remain undetected or not declared.
Promoting international, standardised reporting rules for business
1.10 The government wants to simplify the reporting obligations and minimise compliance costs for digital platforms. Implementing the model rules will provide platforms with a standardised and consistent approach for collecting, verifying and reporting information across different jurisdictions, and will avoid lots of different reporting requirements.
Limiting burdens on business and reporting high-quality and relevant information
1.11 The government recognises that the reporting requirements are an additional burden for platforms, and will look to minimise that burden where possible while also ensuring the rules are workable and effective. The information that platforms will be required to collect, verify and report will only be the information that is necessary to ensure that tax authorities can match taxpayers and use it effectively for compliance purposes. Much of this information is also likely to be collected by platforms as part of their on-boarding process.
Introducing a proportionate but effective penalty regime
1.12 The government will develop a penalty regime to ensure that platforms comply with the rules and report information which is accurate and of high quality by the deadline. Penalties for failure to comply with the requirements of the rules, or for inaccurate or incomplete reports, should be proportionate and an effective deterrent.
Maintaining the UK’s leadership on tax transparency and international cooperation
1.13 The UK plays a leading role in promoting international tax cooperation and transparency, and is one of the first jurisdictions to consult on implementing the model rules. Implementation of the model rules will strengthen international cooperation between the UK and other implementing jurisdictions.
Aim and scope of the consultation
1.14 At Spring Budget 2021 the government announced that it would consult on the implementation of the OECD model rules published in June 2020. As the model rules have already been consulted on and agreed at an international level, the government intends to follow them closely to ensure a consistent and standardised approach. However, there are areas of the model rules which are optional for jurisdictions, or where jurisdictions have some discretion about how they are implemented, such as the optional extension to the sale of goods and transport rental published in June 2021. This consultation sets out the details of the OECD model rules at the start of each section, points out where there is scope for any change, and then presents the government’s proposed approach to implementing the optional or discretionary elements.
1.15 This consultation seeks views on the government’s proposals on those optional or discretionary elements, not on the main rules or their details. It also welcomes comments on the impacts for business from the UK’s proposed implementation of the model rules.
1.16 The final version of the OECD’s rules was published on 22 June 2021, too late to be incorporated into this consultation in time for publication on 20 July (Legislation day). The consultation has been published as soon as practicable, and in line with the government’s commitment to consult over the summer of 2021.
Stakeholder engagement and next steps
1.17 The government would like to hear views from anyone who is affected by or interested in these proposals including individuals, businesses, agents and representative bodies. HMRC will engage directly with existing stakeholder networks and would be happy to have meetings with interested parties. Please contact the lead official if you are interested in meeting to discuss this document.
1.18 Responses and general queries about the content or scope of the consultation can be sent by email to eoi.policy@hmrc.gov.uk, using the subject “Reporting Rules for Digital Platforms”.
1.19 A summary of responses will be published after the consultation closes. The government will also make regulations that will set out the requirements on platforms in the UK rules in detail. A further technical consultation on draft regulations is expected to take place in 2022.
2. Scope and definitions
Key definitions and concepts
2.1 The scope of the OECD model rules is framed in terms of:
- the platforms that have to collect and report information
- the relevant services and goods that are provided
- the persons who provide those services and goods (‘sellers’)
- other definitions relevant to applying the rules
Platforms
2.2 A ‘Platform’ means any software, including a website or app, which allows sellers to be connected to consumers of the goods and services offered by those sellers. This includes third party sellers that provide the goods or services directly to users (customers), as well as platforms that purchase services or goods from sellers and offer them in their own name.
2.3 Platforms may provide services themselves such as operations to collect payments from users and pass them to sellers either before or after they have provided the relevant goods or service. However, software that merely lists or advertises services, or just processes payments, or only redirects or transfers users to another platform does not meet the definition of a platform. This is because it does not immediately facilitate the linking up between sellers and users for the provision of services.
2.4 More specifically, the model rules refer to a ‘Platform Operator’. This is an entity (a legal person or arrangement other than an individual) that contracts with a seller to make all or part of the platform available to the seller, or that collects payments from users for relevant services facilitated through the platform. As part of the contractual arrangements, platform operators will have various legal obligations to know their sellers, so should be well placed to obtain the information from the seller to comply with the model rules.
2.5 Platform operators are subject to the model rules, and are therefore ‘Reporting Platform Operators’, if they:
- are resident for tax purposes, incorporated or managed in a jurisdiction adopting the rules
- have not been specifically excluded
- facilitate the provision of relevant services
Excluded platform operators
2.6 Jurisdictions implementing the model rules can also choose to exclude certain platform operators from the requirements to report information. The model rules include three optional categories of ‘Excluded Platform Operators’. These are platform operators that:
a. facilitate the provision of relevant services for which the total payments (or ‘consideration’) over the previous year are less than 1 million euros, and that make an election to be treated as excluded from reporting
b. demonstrate that the platform’s business model does not allow sellers to profit from the payments received, or
c. demonstrate that they do not have any ‘reportable sellers’ (see paragraph 2.22)
2.7 These exclusions ensure that small-scale platform operators such as start-ups, and those where the risk of any non-compliance with tax obligations by their sellers is very low, do not have to collect information and report it. However, platform operators that fall within the first of the exclusions may also choose to be subject to the model rules if, for example, they expect to grow rapidly and adopting the rules would make future compliance with the rules easier.
2.8 The government wants to ensure that the reporting rules are proportionate and minimise burdens for platforms where possible. The government also wants to promote growth amongst UK start-up companies so does not want to impose additional burdens on small platforms. The government therefore proposes that all three optional categories of excluded platform operators should be incorporated in the implementing regulations, and that platform operators should also be able to choose to opt out of the first of the exclusions in paragraph 2.6.
2.9 The government needs to be able to identify platforms which are not reporting because they are subject to the exclusions (and have chosen to be excluded), so that these platforms are not subject to enforcement procedures. The government therefore proposes that platform operators should be required to indicate if they want to be excluded from the scope of the rules.
2.10 The government envisages that platform operators will be able to indicate whether they fall within the exclusion categories, and hence are exempt from the reporting requirements, as part of the initial registration process, or subsequently if their circumstances change (see paragraph 4.12).
Relevant services
2.11 Only certain services provided by sellers come within the scope of the model rules. These ‘relevant services’ are rental of ‘immovable property’, ‘personal services’ and transport rental if they are provided for a ‘consideration’.
2.12 ‘Immoveable property’ includes residential and commercial property and other fixed property such as parking spaces. Rental includes both short and long-term rentals, irrespective of how the property is held (freehold, leasehold etc.). However, some hotel accommodation is excluded – see paragraph 2.21.
2.13 A ‘personal service’ covers a wide range of services involving time or task-based work performed by a seller, or one or more individuals if the seller is an entity, at the request of a user. It involves work carried out online as well as performed offline at physical locations, and includes the following:
- transport services (such as taxis and private hire)
- delivery (for example, food delivery)
- freelance & professional work (such as accountancy, clerical and legal tasks)
- providing labour (for example, gardening, housekeeping, renovation)
- online services (data entry, IT services, copywriting)
- seasonal and temporary work (such as at restaurants or events)
- services provided by a group of sellers or to several users at the same time
2.14 However, a ‘personal service’ does not include a service provided by a seller who is an employee of a platform operator, or of an entity related to that platform operator, because they will already be subject to PAYE. For these purposes, entities are related if either controls the other or both are under common control. A service also does not qualify as a ‘personal service’ if it is incidental to a transaction, for example, packaging goods which have been sold to a user.
2.15 The model rules allow jurisdictions to include an ‘expansion mechanism’ within the definition of a relevant service to add further categories of services to future proof the rules so that they may adapt as new business models emerge and the sharing and gig economy develops. The government considers that a specific expansion mechanism is not needed as the power to make the regulations for implementing the model rules, which the government introduced in section 129 Finance Act 2021, allows for the regulations to be amended if the model rules are subsequently revised to expand the scope of relevant services.
Consideration
2.16 The model rules define the ‘consideration’ that sellers receive for providing services or selling goods as “compensation in any form that is paid or credited to a Seller in connection with Relevant Services, the amount of which is known or reasonably known by the platform operator.” This can include money, cryptocurrencies, payments in kind, tips, gratuities and incentives paid or credited to a seller. It is considered to be paid to a seller if an amount is paid or credited to an account specified by the seller, even if the account is not in the seller’s name. The amount of consideration paid or credited is after deduction of any fees, commission or taxes withheld or charged by the platform operator; these are reported separately (see paragraph 4.3).
2.17 Sellers may receive consideration for services either directly from customers, or via the platform operator. For example, the platform operator may receive a payment from the customer and then pass it on to the seller. If a platform operator withholds a fee, commission or tax based on amounts paid by customers, the platform operator would be expected to reasonably know the amount received by the seller. However, where the platform operator does not know, or is not reasonably expected to know, the amount that has been paid to the seller for a service, the payment is not treated as ‘consideration’ and therefore the service provided is not a ‘relevant service’.
Sellers
2.18 A ‘seller’ is a user who is registered on a platform to provide relevant services or sell goods. It can be an individual or an entity. Registration is interpreted broadly and can include, for example, where a user has created a profile or account with the platform, as well as being contracted by a platform operator.
2.19 A seller is defined as an ‘active seller’ if they provide relevant services during a reportable period, or are paid or credited during that period. It follows that sellers who are registered with a platform but who do not provide any services or who are not paid for services during a reportable period are not ‘active’, and platform operators do not have to report any information about them.
2.20 Certain sellers present a very low compliance risk as they are usually aware of their tax obligations, are subject to other forms or regulation, or do not represent typical sellers in the gig and sharing economy. The model rules carve out three categories of ‘excluded sellers’ from their scope. These are broadly entities that:
- provide more than 2000 property rentals per year (generally large providers of hotel accommodation)
- are government entities (including local authorities and government agencies), or
- are listed entities, or related entities, whose stock is regularly traded on an established securities market
In addition, as part of the extension of the scope, the amended OECD rules also exclude occasional sellers who make less than 30 sales of goods a year for a total of not more than €2,000 (see paragraph 2.25).
2.21 Although the model rules require platform operators to collect information and carry out due diligence procedures on all their sellers apart from those that are specifically excluded (see Chapter 3), platform operators only have to report information about ‘reportable sellers’. These are defined as active sellers, other than excluded sellers, who are resident or who have rented immoveable property located in a ‘reportable jurisdiction’.
2.22 For the purposes of determining reportable sellers, a ‘reportable jurisdiction’ is one which exchanges reportable information with another reportable jurisdiction. They are expected to be identified in a list published by the OECD which reflects exchange of information agreements. This ensures that information about sellers is collected and exchanged only with the relevant jurisdictions that have implemented the model rules.
2.23 The model rules allow jurisdictions to require reporting on all sellers if this is permitted under domestic legislation. However, the government proposes that UK platform operators should only report information about sellers who are resident in the UK or in another reportable jurisdiction, which avoids platform operators reporting information that will not be used or exchanged by HMRC. The required information includes the seller’s country of residence (see paragraph 4.3) so that the details are exchanged with the jurisdiction in which the seller is resident. For property rentals, UK platform operators will also have to report information about sellers who rent out property in the UK or in other participating jurisdictions. The required information includes the address of the rented property so that the information can be exchanged with the jurisdiction in which the property is located.
Extension of scope
2.24 In June 2021, following consultation with stakeholders, the OECD introduced an optional extension of the model rules that allows interested jurisdictions to implement them with an extended scope to also cover the sale of goods and transport rental. The wider scope is achieved by extending the definition of a relevant service to include the rental of ‘a means of transportation’, and adding a new ‘relevant activity’ to the rules, which includes a relevant service or the sale of goods for a consideration. ‘Goods’ in this context means any tangible property.
2.25 In addition, as outlined in paragraph 2.20, the definition of an ‘excluded seller’ is extended to cover sellers where the platform operator solely facilitated less than 30 relevant activities for the sale of goods and for which the total consideration paid or credited was not more than €2,000 during the reportable period (a calendar year in which the platform operator is required to report). This ensures that ‘casual’ sellers that only make occasional small sales of items are not caught by the extension of the rules.
2.26 The government proposes to adopt the extension as the wider scope will increase the benefits of implementing the model rules for sellers, platforms, and HMRC. The extension broadens the range of sellers that will be helped to comply with their tax obligations and also enables HMRC to detect and tackle tax non-compliance in relation to the additional activities.
Interaction with DAC 7
2.27 In March 2021, the Council of the European Union adopted an amendment to the Directive on Administrative Cooperation (Council Directive 2011/16/EU on administrative cooperation in the field of taxation) known as DAC 7. This amendment extended the European Union’s (EU’s) automatic exchange of information rules to include reporting requirements for digital platforms. DAC 7 is largely based on the OECD model rules published in June 2020 but with a broader scope that includes the sale of goods and transport rental as relevant activities. The new rules will apply from 1 January 2023 and include an obligation for digital platforms, regardless of whether or not they are based in the EU, to provide information about the income of sellers that are located, or whose rental property is located, in the EU. DAC 7 therefore creates obligations for some UK platforms.
2.28 The extension of scope to the model rules to goods gives implementing jurisdictions the option of aligning with the scope of DAC 7. This provides the opportunity for EU and non-EU jurisdictions to exchange information on all relevant activities covered by DAC 7 by implementing the model rules.
2.29 DAC 7 contains a provision to prevent double reporting by platforms which are within the scope of the two sets of rules. It is expected that with the adoption of the model rules extension, UK platforms which fall within the DAC 7 rules can report directly to HMRC under the model rules, rather than reporting to an EU Member State under DAC 7. HMRC would then exchange the information with the tax authority in the relevant EU Member State.
2.30 The government’s aim is to ensure that the reporting requirements minimise burdens for platforms and work well in practice. The government would therefore welcome comments on whether the interaction of the model rules and requirements of DAC 7 would impose any additional burdens on platforms in practice to better understand the impact of the two regimes.
3. Due diligence procedures
3.1 The model rules require platform operators to carry out due diligence procedures to ensure that the information they collect and report about sellers is useful, relevant and accurate for tax authorities. Due diligence processes should also be proportionate and minimise burdens on platform operators where possible. This chapter sets out the various due diligence procedures that the model rules require platform operators to carry out, discusses the options for some of the information that has to be provided, and sets out the government’s proposals for optional elements of the requirements.
Identification of excluded sellers
3.2 Some sellers are excluded from the scope of the model rules (see paragraph 2.20). Platform operators will therefore need to identify which of their sellers are excluded and not subject to due diligence and reporting. The method they will use to do so depends on the type of excluded seller.
3.3 The model rules state that platform operators may rely on their available records of sellers and property listings to determine if a seller qualifies as an excluded seller if they are:
- an entity that provides more than 2000 property rentals per year (generally large-scale hotel businesses who are likely to be aware of their tax obligations), or
- an occasional seller who has undertaken less than 30 sales of goods and for which they were paid not more than €2,000 for the reportable period
This determination can be done at the end of the reportable period, for example, on the basis of the actual transactions carried out. Alternatively, platform operators may put other procedures in place at an earlier stage to determine if any of their sellers are likely to meet the exclusion criteria. For example, if a seller has consistently made significantly more than 2000 property rentals each year and is likely to continue to do so, the platform operator may decide that the seller will qualify as an excluded seller at the start of the reportable period.
3.4 For government and listed entities, platform operators may rely on publicly available information or on a confirmation from the entity seller to determine whether they meet the conditions for this type of excluded seller.
Collection of seller and rental property information
3.5 The model rules set out the information that platform operators will be required to collect for all sellers, other than excluded sellers. The type of information to be collected depends on whether the seller is an individual or an entity, and the nature of the activity carried out by the seller.
3.6 For each individual seller, the required information is:
- first and last name (and middle name if provided)
- primary address (usually their home address, unless the platform only collects a billing address)
- tax identification number (TIN) and the jurisdiction which issued it
- date of birth
3.7 For each entity seller, the required information is:
- legal name
- primary registered office address
- TIN and jurisdiction of issue
- business or company registration number (if different from the TIN)
3.8 Where a seller provides property rental services, platform operators are also required to collect the address of each property listing. For this purpose, ‘property listing’ means all immovable property units, including rooms, apartments, houses or other forms of fixed property, at the same street address and offered by the same seller. For example, multiple rooms in a hotel or separate apartments in a building with a single street address are treated as a single property listing. Platform operators should usually be aware of rental property details as they will provide this information to users; but if not they will need to put procedures in place to collect and verify the address of the property.
3.9 The information to be collected reflects its importance and use by tax authorities to identify sellers and match them to details held on their databases, and to determine the residence of the seller or the jurisdiction in which a rental property is located. For example:
- the date of birth is important to ensure that individuals who may have the same or very similar names living at the same address can be distinguished and matched to their tax records
- a TIN will enable a tax authority to identify an individual or entity and match them with their tax records (see paragraphs 3.10 to 3.17)
- the primary address will be used to determine where an individual lives or where an entity’s registered office is located to determine the residence of a seller and link them to a jurisdiction for reporting purposes (see paragraph 3.21)
- the address of a rental property will be used to identify the jurisdiction where it is located so that information about the seller can be sent to the appropriate country
Tax Identification Number (TIN)
3.10 The TIN is a unique number, or number/letter combination, which enables an individual or entity to be identified and matched with their tax records. It provides a convenient and more reliable method for matching taxpayers than using a name (which may not be unique) and address (which could be out of date or incorrect). The TIN must be issued by the jurisdiction where the seller’s primary address is located so that it can be used by that jurisdiction on receiving the information to link the seller to their taxpayer databases. Some jurisdictions issue a TIN to all taxpayers. Where a jurisdiction does not issue a TIN, another functionally equivalent number can be provided instead, such as a social security number or personal registration number.
3.11 The model rules do not specify which type of reference number should be used as a TIN as this will be different for each jurisdiction. For UK resident sellers there are several possible options for a TIN – a Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR), National Insurance number (NINO), Company Registration Number (CRN), VAT Registration Number (VRN) or a bespoke registration number/code. The government is currently minded to propose that platform operators can report a TIN from a range of options for UK resident sellers. This is because there does not seem to be an ideal TIN to use for both individuals and entities, and each option has advantages and disadvantages.
For individuals
3.12 A NINO can be used to match an individual’s personal data to their tax record and can be shared with third parties in some cases so it could be a suitable TIN. Although NINOs are commonly used, they are still sensitive pieces of information so platform operators will need to ensure that the details are held securely and not disclosed inappropriately. However, some UK sellers may not have a NINO; for example, if they are not employees or self-employed, or do not claim benefits, or if they do not have a specific reason to be issued with a NINO. This is only likely to apply to a very small number of individuals who provide property rental services but it nonetheless creates a difficulty as such individuals will not be able to obtain a NINO and provide one as a TIN.
For entities
3.13 For UK companies and other entities, the CRN is already held on HMRC’s systems and can be used effectively for matching purposes. It is also in the public domain at Companies House. The CRN therefore seems to be an obvious choice for a TIN for UK sellers who are entities but it will not be relevant for individuals, or for some companies operating through a platform who were incorporated, or are resident, outside the UK.
For individuals and entities
3.14 UK sellers who are self-employed or within Self Assessment for another reason are very likely to have a UTR, which could be used to accurately match their details with their tax records. This could be an option for individuals who do not hold a NINO. Although as a general principle HMRC advises taxpayers not to disclose their UTR to anyone to help protect customers from fraud and identity theft and prevent unauthorised access to HMRC systems and records, UTRs are reported and exchanged in other exchange of information agreements, such as the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) for financial accounts. Platform operators would need appropriate levels of security to keep the UTR details protected and secure.
3.15 Another option for a TIN is the VRN if it is available. This is also in the public domain so presents fewer disclosure risks than a NINO, and can be checked to see if the number is valid and the name and address of the business is correct. However, UK sellers who are not registered for VAT will not have a VRN. In some circumstances there is more than one VRN associated with a business, so it may not be very effective for matching purposes.
3.16 A possible alternative option that the government is exploring is to introduce a new ‘verification’ service for the purposes of the model rules (see paragraph 3.26) which sellers could use to generate a bespoke code or reference number that could be used as a TIN. This option would have the advantage of applying to all UK sellers and has the lowest disclosure risk since the reference number/code would not be used for any other purpose. On the other hand, it would create another reference number that sellers would need to note. If the government was minded to introduce a verification service it would take time to implement and it may not be available when the rules are currently expected to come into force in January 2023.
3.17 The government is keen to hear from both platforms and sellers on which one or more options above would be a good choice for a TIN.
Verification of seller information
3.18 The model rules require platform operators to verify the information provided by the seller to make sure it is accurate and reliable. This must be done using all available records including information already collected or maintained for on-boarding, payment, regulatory or other commercial purposes. For example, the name of a seller must be verified against government identification documents the platform operator holds, as well as cross checking the details with financial records, emails or other available information. Likewise, a seller’s address and country where the TIN is issued must be verified against transactional records that can identify and confirm where the seller is resident. Such checks should take into account other relevant information that show the link between the seller and jurisdiction, such as a local IP address. Platform operators should also use any publicly available checking tools or verification services to confirm the validity of a TIN such as a CRN or VRN.
3.19 Where sellers are already active before the rules are implemented or the platform operator is required to report, the verification of collected information may be done using available existing electronically searchable records. If some of the information is no longer reliable, for example, when an address becomes out of date because the seller has moved, the platform operator is required to collect new information or documentation to correct or update the details. That new information also has to be verified using all available records so that the platform operator can show that all the data collected about a seller is reliable, up to date and accurate.
3.20 In some cases, a platform operator may be informed by a tax authority that certain previously collected and verified data is inaccurate. This could happen, for example, if a tax authority has received data on a seller following an exchange of information and cannot match a record to the taxpayer, or it has some other reason to believe the information is inaccurate. In these cases, the platform operator must collect the relevant information again and verify it using reliable independent documents or data.
Determination of sellers’ jurisdiction of residence
3.21 Once collected information has been verified, platform operators will need to determine the jurisdiction of residence of a seller so that it can be reported to the appropriate tax authority. The model rules explain that the jurisdiction of residence of a seller is usually the jurisdiction in which the seller’s primary address is located. In most cases the primary address will be the seller’s home address (for individuals) or registered office address (for entities). A platform operator should therefore be able to determine a seller’s jurisdiction of residence from their home or registered office address.
3.22 Alternatively, if a Government Verification Service is available (see paragraph 3.26) in the jurisdiction where the seller has their home or registered office address, the platform operator may be able to use it to determine a seller’s jurisdiction of residence. The platform operator should be able to use the service to confirm the seller’s name and primary address. That address will then determine the seller’s jurisdiction of residence.
Government Verification Service (GVS)
3.23 The model rules require platform operators to collect from sellers the information listed in paragraph 3.6 and 3.7. The only exception to this is where a jurisdiction provides a ‘Government Verification Service’. This is an electronic process that is made available by a jurisdiction and allows platform operators to confirm the identity and/or residence of a seller. It may include the use of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) which are a type of software that connects computers or applications so they can ‘talk’ to each other.
3.24 It is up to a jurisdiction to decide on the appropriate scope for a GVS for these purposes. As an illustration, the commentary (See paragraph 63 on page 19 of the Model Rules) on the model rules proposes one possible process for a GVS identification method:
a. a reporting platform operator identifies that a seller is linked to a GVS jurisdiction during its on-boarding process and directs the seller to the GVS portal
b. the seller provides their details (for example, a TIN or user name) which enables the GVS to identify the seller
c. the jurisdiction/GVS provides the reporting platform operator with a unique reference number/code
d. the platform operator includes the number/code in the information they report allowing the jurisdiction receiving that information to match it with their seller database
3.25 Separately, HMRC is introducing a ‘tax check’ that will take place when people renew their licences to drive taxis or private hire vehicles, or deal in scrap metal. A new digital service is being developed to enable individuals and companies in these sectors to do the tax check and obtain a code, which will be used by the licensing body to obtain confirmation from HMRC that the licence applicant has carried out the ‘tax check’. Broadly, the service is expected to work as follows:
- The applicant will use the digital service to provide some basic information about themselves, their licence and their tax situation to complete the tax check
- If the details match the ones held by HMRC’s systems, the applicant will be given a tax check code, which they will give to the licensing body with their application
- The licensing body will be able to access the service using the code and the applicant’s ID details and licence type to get confirmation that they have completed the tax check
3.26 The government is considering whether this ‘tax check’ service could be adapted and used as a GVS since it has many of the features outlined in the process proposed in the model rules commentary. For example, a seller might be able to use a similar digital service to provide their personal details which would be checked against information about the seller held by HMRC systems. If there was a match, the seller would be given a unique code which they could pass to their platform operator. The platform operator would be able to use the code to access the service to confirm the identity and address of the seller, thus avoiding the need to verify that information with its own records. The unique code could also be used as a TIN (see paragraph 3.16) and could be reported to HMRC in order to match the seller with their tax records.
3.27 There is no suggestion that a seller would be required to use the service and get a code in order to become a seller, or to provide services or sell goods on a platform. Even if the government is minded to implement a GVS, then it may not be developed in time to be available from the start of implementation.
3.28 The government welcomes comments on whether platforms, sellers and other stakeholders would make use of such a service if it was available, or if they would prefer to collect and verify the information by a different method, and any potential practical issues a GVS might create.
Timing and validity of due diligence procedures
3.29 The model rules also state that platform operators must complete the due diligence procedures by 31 December of the reportable period. This is defined as any calendar year in which a platform operator must report under the rules as a reporting platform operator. However, the model rules provide some flexibility around timing for new reporting platform operators and processes for established platform operators.
3.30 For entities who become reporting platform operators for the first time (due to the introduction of the rules, or because they are a new platform, or are no longer an excluded platform operator), the due diligence procedures outlined above are only required to be completed by 31 December of the second reportable period in which the platform operator is subject to the reporting rules. This is to ensure platforms have enough time to collect and verify the required information and build the relevant IT systems. The extended deadline means that, for example, if a platform becomes a reportable platform operator in January 2023 (so their first reportable period is the year ended 31 December 2023), it must complete the due diligence procedures by 31 December 2024. However, some platform operators may wish to complete their due diligence procedures and report the information to tax authorities and/or sellers earlier than this extended deadline.
3.31 The rules also acknowledge that collected and verified information about sellers or their residence status may remain unchanged over time. Platform operators may therefore rely on due diligence procedures for previous reportable periods provided that:
- the primary address of each seller has either been collected and verified or confirmed in the last 36 months
- the reporting platform operator does not have any reason to believe the info collected is incorrect or unreliable
This confirmation could be made by, for example, a statement from the seller that their previously collected address is still valid.
Application to active sellers
3.32 The model rules provide an option for completing the due diligence procedures only for active sellers in a reportable period (see paragraph 2.19). This means that platform operators can choose to collect and verify seller details and determine their residence from the date that a seller provides a relevant service or sells goods or is paid for those activities. In other words, platform operators can opt not to carry out due diligence procedures for new sellers who have only just registered with the platform or for existing sellers who are not active. The government supports this option to reduce administrative burdens for platform operators and will include the relevant provisions in the regulations.
3.33 Platform operators who make use of this option should have procedures and enforcement measures in place to ensure that all active sellers have provided the required information by 31 December of a reportable period. The model rules suggest that these measures could, for example, include mechanisms to prohibit undocumented sellers access to the platform or withhold payment from such sellers until they provide the information. However, the government considers that it is the responsibility of platform operators to decide what enforcement measures are appropriate and does not propose any additional requirements to compel platform operators to put such measures in place (see paragraph 5.14).
Due diligence by third parties
3.34 Platform operators may also rely on an independent third party service provider, including another platform operator, to carry out the due diligence procedures, especially if they have better resources or technology to do so. This takes into account the situation where platforms use a number of platform operators to provide different services or functions in one or more jurisdictions. For example, one platform operator may provide access to the platform’s website, while another platform operator may collect payments from users. Where there is more than one platform operator in respect of a platform, any of the platform operators may carry out the due diligence procedures in respect of all or a defined group of sellers. This arrangement avoids duplication of the due diligence processes by multiple platform operators with respect to the same platform.
3.35 In order for a platform operator to rely on a third party to perform the due diligence, it should put appropriate contractual arrangements in place to ensure that:
- information needed to complete the procedures is available to the third party service provider
- the platform operator can obtain any information collected and verified on sellers from the third party provider
Even if due diligence procedures are carried out by another platform operator or third party service provider, the reporting platform operator remains responsible for their completion and must be able to demonstrate compliance with the due diligence requirements.
3.36 Where a platform operator carries out due diligence procedures for a reporting platform operator in a different jurisdiction, it can rely on the rules in its own jurisdiction provided they are substantially similar to the ones in the other country. This ensures the due diligence procedures are consistent across a number of jurisdictions.
4. Reporting information
4.1 The model rules require platform operators to report certain information to tax authorities so that it can be exchanged with other tax authorities, or used by a tax authority for its own compliance purposes, and also given to the sellers to help them comply with their tax obligations. The rules, and this chapter, set out:
- the details of the information that must be reported about the platform operator, sellers and property rentals
- the manner in which the information has to be reported
- the deadlines for reporting the information to tax authorities and sellers
- the circumstances in which information does not have to be reported
Information to be reported
4.2 Each reporting platform operator must provide the following identification information:
- their name, registered office address and TIN
- the business name(s) of the platform(s) in respect of which they are reporting
4.3 For each reportable seller who has provided ‘relevant services’ other than immoveable property rental (see paragraph 2.10), a reporting platform operator must report the following information to identify the seller and the jurisdiction that they are linked to for reporting purposes, and to provide details of the payments made to them:
- details of the seller (see paragraphs 3.6 and 3.7)
- any other TIN available to the reporting platform operator, such as a VAT number
- the ‘financial account identifier’ – if this is available (see paragraph 4.5)
- the name of the holder of the account to which payments are made – if this is different to the name of the seller and available – and any other available identifying information
- the country in which the seller is resident on the basis of their address (see paragraph 3.21)
- the total ‘consideration’ paid (see paragraph 2.16) during each quarter of the reportable period and the number of services for which it was paid
- the amount of any fees, commission or taxes withheld or charged by the platform operator during each quarter
4.4 For each reportable seller who has provided immoveable property rental services, a reporting platform operator must report the following information:
- the information listed in paragraph 4.3
- the address of each property listing (see paragraph 3.8)
- the number of rentals with respect to each property listing
- the number of days each property listing was rented during the reportable period and the type of listing – if available
Bank account information
4.5 The ‘financial account identifier’ is a unique identifying reference or number (e.g. IBAN, sort code and account number) of the seller’s bank or other account to which payments are made. These account details are very reliable items of information for taxpayer matching purposes since they are likely to be correct if payments are made to the account. However, not all tax authorities can use this information to match sellers. The model rules therefore set out that the details only have to be reported if they are available to the reporting platform operator, or another platform operator using the same platform, and are requested by a tax authority who can use the data for matching purposes. Jurisdictions whose tax authorities can use the details for such purposes, and who opt in to receive the information before it is exchanged, will be included on a published list so that platform operators will be able to determine if sellers’ bank details need to be reported.
4.6 The government proposes requiring that a seller’s bank account details, or details of another account to which payments are made, are reported if these are available to the platform operator (or to a related platform operator). Financial account information supports good data matching and has been used effectively to improve matching processes. The government is aware of the sensitivity of this information. As for other exchanges of information which involve bank details, such as CRS, the data will be held securely in line with the HMRC Records Management and Retention Policy and any sharing of personal data will follow the relevant guidance and legal requirements (see the International Exchange of Information Manual (IEIM100010)).
4.7 Bank account details, and other reported information, will be exchanged with other tax authorities under international treaties which contain strict secrecy requirements to ensure customer data is safe and secure. In addition, exchanges of information will only take place with treaty partners who have appropriate confidentiality and data safeguards in place. These safeguards are evaluated using, for example, the Information Security Management work that monitors and reviews the Standard for Automatic Exchange of Financial Account Information in Tax Matters (see Confidentiality and Information Security Management toolkit).
Other information
4.8 During discussions with the OECD, some platforms indicated that they may be able to provide additional information about a seller, such as their mobile phone number, if tax authorities found this helpful. The government would not require these additional details to be provided as this would be inconsistent with the standard information that the model rules require. However, the government is considering whether other information about a seller could be provided on a voluntary basis, if platforms already collect this information, providing that the schema for submitting and exchanging the required information allows these additional details to be reported.
Form of reporting
4.9 The information specified above must be reported in a standardised OECD Sharing and Gig Economy XML Schema. This ensures maximum compatibility of the IT formats used for reporting information by platform operators, and for tax authorities to use that data. The schema is currently being developed at the OECD and details will be available to platform operators once they are published.
4.10 Information about the amount of consideration must be reported in the currency in which it was paid or credited. If the consideration is paid in some other form than government-issued or fiat currency, the amount should be reported in the local currency, converted or valued in a manner that is consistently determined by the platform operator.
Online service
4.11 HMRC will develop an online service to enable platform operators to report the required information. This is expected to be similar to the existing service for reporting to HMRC under Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI) agreements, such as CRS. Currently, this service enables financial institutions and their agents to register for AEOI, and then to either upload an XML file with the required information, or to create an online return and enter the information manually. It also allows customers to amend the information if necessary and update the relevant contact details. Reporting platform operators will be able to register, report and amend information in a similar way.
4.12 The government is considering only offering the option to submit reports directly to HRMC in an XML file format, as this is the mechanism currently used for most other AEOI reports, and not including the option to enter reportable information manually in the online service for reporting the information required by the model rules. The government is also exploring whether to offer an option of using an Application Programming Interface (API) to seamlessly transfer the relevant information from a platform operator’s IT system to HMRC’s systems.
Registration and nil returns
4.13 It is expected that all UK reporting platform operators, as well as UK excluded platform operators (see paragraphs 2.5 to 2.7), will have to register on the new online service to indicate that they potentially fall within the scope of the model rules. Although excluded platform operators will still have to register, they will be able to indicate at the beginning that they are exempt from the reporting requirements and do not need to do anything else. This will enable a distinction to be made between platform operators who have not reported anything because they are exempt from those that have not reported due to a failure to comply with their reporting obligations.
4.14 The model rules allow a jurisdiction to require the filing of nil returns to indicate that a reporting platform operator did not identify any reportable sellers during a reportable period. The government considers that reporting platform operators should indicate that they are submitting nil returns for a particular reporting period. This could be because, for example, they have only recently started to operate as a platform and do not yet have any reportable sellers. A nil return would distinguish between reportable platform operators who have not submitted any information because they have nothing to report from those that have not done so because they have failed to comply with their reporting obligations. It also enables a distinction to be made between reporting platform operators who do not report any information and excluded platform operators who are not required to report anything. To minimise administrative burdens, it is envisaged that nil returns could be made simply and quickly by confirming the position at the start of the online reporting process.
Reporting deadlines
4.15 Reporting platform operators must report all the required information about the platform operator and each reportable seller (see paragraph 2.21) to the tax authority of the jurisdiction in which the platform operators are resident for tax purposes, or in which they are incorporated or managed if they do not have a tax residence. UK resident (or incorporated/managed) platform operators will therefore report to HMRC. The model rules specify that the reporting deadline for any reportable period is 31 January of the year following the calendar year in which a seller is identified as a reportable seller (the ‘reporting date’).
4.16 New reportable platform operators may not be able to identify a reportable seller until the second reportable period when their due diligence procedures are completed (see paragraph 3.30). In such cases, the required information would not have to be reported until 31 January of the year following that second reportable period.
4.17 Platform operators are also required to provide the information relating to each reportable seller to that seller by the same 31 January reporting date. This will help sellers to work out their total income and fill in their tax returns. However, in some cases, the information about income may be given to sellers at the same time as the deadline for filing their UK Income Tax Self-Assessment tax return (which is also 31 January). This will only apply where sellers need to complete tax returns and have accounts for income tax purposes for a period (an ‘accounting period’) which ends between 1 January and 5 April. In these cases, the information about the seller’s income for the period from 1 January will come from a later reporting period. This is illustrated by the following example.
Example:
Seller S receives income from providing services on a platform P and is liable to UK income tax on the trading profits derived from this income. He includes the income in his accounts which are made up each year to 31 March. He has no other income and his taxable platform income for the year ended 31 March 2026 (that is, for the accounting period 1 April 2025 to 31 March 2026) must be included on his 2025 to 2026 Self Assessment tax return. The deadline for submitting this return is 31 January 2027.
Platform P provides S with statements of his income each year. For the reporting period ended 31 December 2025, P provides S with a statement on 31 January 2026. S can use this statement to work out his income for the period from 1 April 2025 to 31 December 2025 but not for the period from 1 January 2026 to 31 March 2026. To do that, S has to wait until P provides him with a statement for the reporting period ended 31 December 2026, which includes the income for the period from 1 January 2026 to 31 March 2026. P provides the statement on the next reporting date on 31 January 2027, but this is the same as the filing date for the 2025 to 2026 tax return and is too late if S wants to file his return earlier, as shown in Figure 1 below.
Figure 1
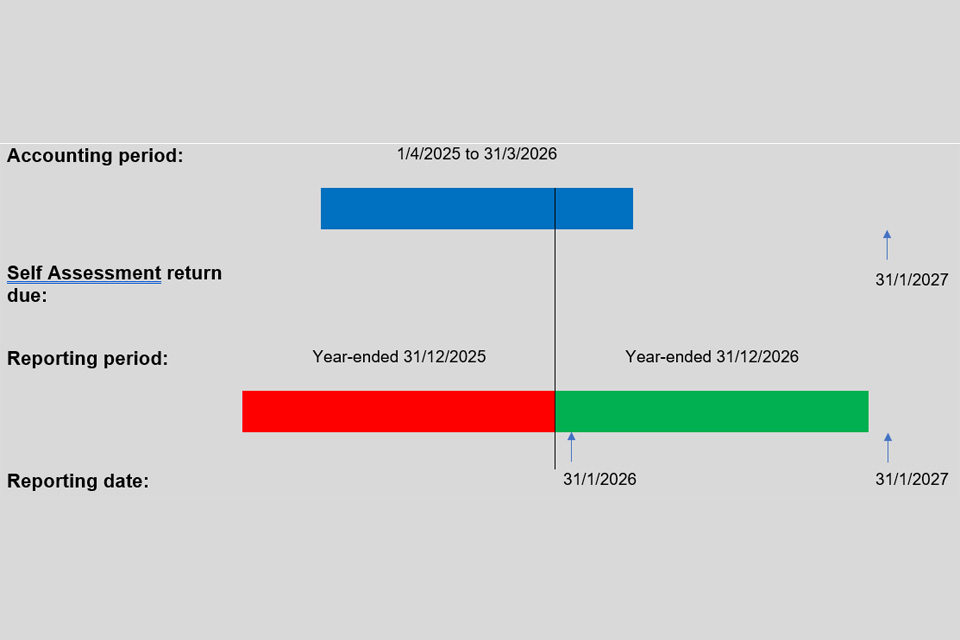
4.18 The government is keen to make the information about income as useful as possible for sellers. The government is not proposing a change to the reporting date but would like to hear from platforms about any flexible solutions to how they may provide reports to sellers ahead of the 31 January reporting date. As platform operators have to report the amount of consideration paid to each seller during each quarter of the reportable period, the government would be interested in whether platforms would be able to, for example, send reports to the sellers on a more frequent basis (such as monthly, quarterly, half-yearly). This could be an option which ensures that the information is as useful for sellers as possible, whilst minimising burdens for platforms.
Information for sellers
4.19 The details that platform operators must provide to each reportable seller, including the total amount paid to them, should help sellers to work out how much income they have received from providing their services and/or selling their goods on the platforms they use. This in turn should help them to declare that income correctly on their tax returns and comply with their tax obligations, providing they get the information before they need to submit their tax return.
4.20 However, some sellers may be unaware of their tax obligations, and may not realise that the income from providing their services or selling goods using a platform is taxable and has to be declared on their tax return, particularly if that income is in respect of assets held abroad such as a rental property. Some may also not be aware of available reliefs and exemptions, such as the Trading Income Allowance (note: total receipts from self-employment and miscellaneous income of up to £1,000 are exempt from tax and generally do not need to be reported on a tax return). The working relationship and interactions between a seller and the platform operator also presents an opportunity for the platform operators to tell sellers about potential tax obligations as part of any general information given to new sellers during on-boarding or in periodic updates for existing sellers. Because of the closer relationship, some sellers may also prefer to approach a platform operator regarding any tax consequences of providing their services or selling goods on the platform rather than refer to official HMRC or government guidance.
4.21 The OECD’s Code of Conduct, which has some areas of overlap with the model rules, encourages platform operators to engage with their sellers to help them understand their tax obligations and report taxable income to their tax authority. In addition to providing each seller with an annual notification of payments received from platform transactions, the Code suggests that platform operators should:
- send each seller a statement on their responsibility to meet their tax obligations
- direct sellers to guidance issued by the tax administration of their jurisdiction of residence (or where immoveable property is located, if appropriate)
The Code of Conduct also places an obligation on tax authorities to provide information setting out the circumstances when sellers may be liable to tax, including details of any thresholds, exemptions, allowable expenses and reporting obligations.
4.22 Although some platforms already provide excellent guidance about tax obligations and potential tax liability on their websites, the government would like more platform operators to draw sellers’ attention to the tax consequences of providing services or selling goods on their platforms and to direct them to the appropriate guidance for further details. The government is not proposing that platform operators should provide tax advice to sellers, but it would like to explore if more can be done to ensure that sellers are sufficiently aware of taxation consequences to seek further advice and guidance as required. This is particularly relevant to complex areas such as the taxation consequences of assets held or income arising overseas.
4.23 HMRC is keen to work with platform operators to help them to provide relevant tax information for their sellers, or to direct sellers to the appropriate guidance on GOV.UK, so that sellers understand the tax consequences of providing their services and know what they should do to comply with their tax obligations. In addition, HMRC would like to use the data about sellers to help them comply with their tax obligations and correct any non-compliance, particularly in the light of the recent discussion document about helping taxpayers to get their offshore tax right. The government welcomes views on how HMRC might do that, including any suggestions for collaborative working with platform operators and other stakeholders on suitable guidance, particularly for overseas platforms who may not be familiar with UK tax rules.
Avoiding duplicate reporting
4.24 A reporting platform operator does not have to report information about a seller if another platform operator will be reporting the required information about that seller. The reporting platform operator must obtain adequate assurances from the other platform operator that it will report the required information. This could be done by a written confirmation or agreement, and mechanisms should be put in place to ensure that the reporting obligations are performed effectively. This arrangement avoids duplicate reporting in situations where there is more than one reporting platform operator in respect of the same seller. However, the arrangement does not apply in respect of a seller who is resident in either:
- the same jurisdiction as the reporting platform operator, or
- in a jurisdiction that does not have an exchange agreement with the jurisdiction (that is, it is not a partner jurisdiction) of the other platform operator
Example:
A platform is operated by two platform operators: PO1 is resident in the UK and PO2 is resident in the US. The platform is used by 2 sellers: seller A is resident in the UK, and seller B is resident in France which is a partner jurisdiction of the UK and the US. PO1 relies on PO2 to carry out the due diligence procedures since PO2 provides the on-boarding functionality.
- PO1 must report information about seller A to HMRC because seller A is also resident in the UK
- PO1 does not have to report information about seller B to HMRC providing it gets an adequate assurance from PO2 that it will fulfil the reporting obligations with respect to seller B
- PO2 must report information about seller B to the US tax authority who will exchange it with France
4.25 The rules also suggest that jurisdictions may consider introducing an obligation that both the platform operator transferring their reporting responsibility and the platform operator taking it over notify their tax administrations of the arrangement. The government proposes that a simple process is introduced as part of the new reporting service for notifying HMRC when arrangements to transfer reporting obligations to another platform operator for a particular reporting period have been made. A notification process would also avoid any unnecessary possible penalties for not reporting if a platform operator has already made arrangements for another platform operator to report the required information.
5. Administration and enforcement
5.1 Jurisdictions implementing the model rules are expected to have rules and administrative procedures in place to ensure effective implementation and compliance with the due diligence procedures and reporting requirements set out in the rules. While the model rules have some guidance on the types of enforcement procedures that are expected to be in place, jurisdictions have discretion to determine the precise details of any penalty or enforcement regime taking into account the existing compliance framework in that jurisdiction as well as the expected procedures set out in the guidance.
5.2 This chapter sets out the government’s initial views on what the UK’s penalty and enforcement regime should be like, and invites views on the proposed approach to ensure that it is effective whilst also being reasonable and proportionate. The proposed penalties fall into two broad types:
- one-off single penalties for reporting incorrect or incomplete information
- initial and continuing daily penalties for failing to comply with the collection, verification, reporting and other requirements in the model rules
Reporting of incorrect or incomplete information by a platform
5.3 It is important that the information collected, reported and exchanged under the model rules is complete and accurate. The model rules therefore expect jurisdictions to develop procedures to discourage reporting platform operators from reporting incorrect or incomplete information and take appropriate follow up action if they do. Incorrect information may be reported if a platform operator does not implement adequate due diligence processes to ensure that the seller details are correct, or fails to take care when reporting. Information may be incomplete if certain data items are missing because, for example, a seller has not provided the required information.
5.4 Given that the effectiveness of the rules relies on good quality information, the government considers that a platform operator should be liable to a penalty for providing incorrect or incomplete reportable information. This approach would also be consistent with existing penalties where a financial institution provides inaccurate information in relation to the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) or the US Foreign Account Tax Compliance (FATCA) reporting obligations (see Regulation 15 of The International Tax Compliance Regulations 2015), and Country-by-Country (CBC) Reporting (see Regulation 14 of The Taxes (Base Erosion and Profit Shifting)(Country-by-Country Reporting) Regulations 2016).
5.5 Penalties should be sufficiently high to act as a deterrent and be effective at compelling compliant behaviour, yet should also take into account exceptional circumstances or the reasons for the failure or non-compliance. The government also recognises that it will take some time for platforms to adjust to the new rules and wants to be reasonable and proportionate in its approach to penalties.
5.6 The government proposes that a platform operator should be liable to a penalty for reporting inaccurate or incomplete information up to an appropriate maximum amount for each report, but that amount should be reduced for a number of mitigating factors. These could include, for example:
- the scale of the inaccuracy or omission
- the behaviour leading to the error (for example, whether it is deliberate or an accidental oversight)
- the previous history of good compliance, or any failure or non-compliance
- the degree of co-operation in identifying, disclosing and correcting the inaccuracy/omission
- the timescales involved
- the size of the business so that the impact of the penalty is proportionate
The government considers that this approach would be fairer, more proportionate and more effective than imposing a fixed amount penalty regardless of circumstances. The government welcomes views on this approach, the amount that would be appropriate for a maximum penalty, and comments on whether any other factors should be taken into account.
Failure to comply with reporting and other requirements
5.7 Jurisdictions are also expected to introduce effective enforcement provisions to address non-compliance with the collection, verification and reporting requirements in the model rules. This may include using existing rules that provide for the imposition of fines and penalties for failing to comply with particular requirements set out in legislation.
5.8 For other reporting regimes, such as CRS, FATCA, CBC and disclosable arrangements under the amendment to the EU Directive on Administrative Co-operation (DAC6), where the various requirements are set out in regulations, the penalty provisions are triggered by a failure to comply with the relevant regulations or obligations. Since the collection, verification, and reporting requirements of the model rules will also be set out in regulations, the government considers that penalty provisions could also be activated if a reporting platform operator fails to comply with those regulations. This could happen, for example, if a platform operator fails to report the required information by the deadline, does not collect or verify the required information, or fails to keep records (see paragraph 5.12).
5.9 The CRS and CBC penalties for failing to comply with the relevant regulations consist of an initial penalty for the first failure, and continuing daily penalties for continuing failure after the initial penalty has been assessed. The DAC6 regulations (the International Tax Enforcement (Disclosable Arrangements) Regulations 2020) also provide for daily penalties from the outset if the initial penalty appears to be too low. While this approach is meant to encourage prompt compliance, it is only effective if the amount of the initial and daily penalty is sufficiently high to act as a deterrent.
5.10 In line with the proposed approach for penalties for reporting inaccurate or incomplete information, the government proposes that both initial and continuing daily penalties for failing to comply with the model rules regulations should be up to an appropriate maximum amount, although this would be reduced to take into account various mitigating factors as explained in paragraph 5.6. The government welcomes views on this approach, the amount that would be appropriate for a maximum initial and continuing daily penalty, and whether the proposed approach would be more effective than the current CRS, CBC and DAC6 penalties.
Record keeping requirements
5.11 The model rules guidance includes an expectation that jurisdictions will introduce rules requiring platform operators to keep records of steps undertaken and any information relied on for due diligence procedures and reporting. Such records should be available for at least 5 years following the end of the reporting period, and should be made available to a tax authority if requested.
5.12 The government proposes including the requirements in the previous paragraph to keep records and make them available to HMRC on request (when reasonably required to determine if the obligations in the regulations have been complied with) in the regulations. Failure to keep records or to provide the information would trigger the relevant penalty provisions as discussed in the previous section.
Other enforcement matters
5.13 The government recognises that sometimes there will be valid reasons why a platform operator is unable to meet various obligations. The government therefore proposes that a liability to a penalty should not arise if a platform operator can show that there was a reasonable excuse for failing to comply with the regulations or for providing inaccurate or incomplete information. As with other penalties, the platform operator will be able to appeal against a penalty determination in writing to the independent tax tribunal, giving grounds for the appeal.
5.14 The guidance on enforcement of the model rules expects that jurisdictions will have rules requiring reporting platform operators to enforce the due diligence collection and verification requirements. It gives examples where platforms may prevent sellers from connecting to consumers via the platform or may withhold payment for their services if they do not provide the required information. The government expects platform operators to put appropriate contractual arrangements in place with their sellers to ensure that they provide the relevant details so that the due diligence requirements are met. The government does not propose any additional requirements to compel platform operators to put those contractual or other arrangements in place, since the proposed penalties would apply if due diligence procedures are not carried out correctly.
5.15 Finally, jurisdictions are expected to introduce administrative procedures to verify compliance with due diligence and reporting requirements. HMRC already has administrative procedures to check that the information received from financial institutions and other reporting entities is accurate, complete and reported by the required deadlines. These procedures will also apply to information received from platform operators. In addition, the requirement to keep records and provide information as required to HMRC (see paragraph 5.12) should ensure that platform operators comply with their obligations. The government therefore does not consider that any other administrative procedures are needed to meet this expectation.
5.16 The government welcomes views on whether the proposed penalty approach is reasonable, proportionate and effective in ensuring that platform operators comply with the model rules and that the rules are implemented effectively. The government will consider stakeholder views in determining the details of the penalty regime and will include further details in draft regulations when they are published for consultation.
6. Assessment of impacts
The summary of impacts below was published at Spring Budget 2021 as part of the Tax Information and Impact Note for the measure on Reporting rules for digital platforms.
Exchequer impact (£m)
| 2020 to 2021 | 2021 to 2022 | 2022 to 2023 | 2023 to 2024 | 2024 to 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empty | Empty | Empty | Empty | Empty |
The final costing will be subject to scrutiny by the Office for Budget Responsibility and will be set out at a future fiscal event.
Economic impact
This measure is not expected to have any significant macroeconomic impacts.
Impact on individuals, households and families
The measure is not expected to have an impact on individuals who use digital platforms to buy goods or services.
This measure is not expected to have an impact on family formation, stability or breakdown.
Equalities impacts
It is not anticipated that there will be impacts for groups sharing protected characteristics.
Impact on businesses and Civil Society Organisations
This measure is likely to significantly increase customer costs for some of the platform businesses affected. HMRC is working to understand these costs and the scope of any impacts better.
The consultation process will also enable HMRC to establish the costs with more certainty.
Digital Platforms
This measure is expected to have a significant impact on UK digital platform businesses who will have to collect specific pieces of information about sellers, which some platforms will not already collect. UK platforms will have to verify that information using third party documentation, collate and report that information to identify the residency of the seller and the jurisdiction in which a property is located.
There will be one-off costs which will include familiarisation with the change and could also include updating their website/software to collect more information, updating their IT and upskilling staff to provide information to tax authorities in XML schema format, upskilling staff to implement the new information collection and verification processes, and communicating the changes to sellers using the platform.
Continuing costs could include digital platforms collecting more information than they currently do now from sellers on their platforms and sending that information to HMRC annually.
Customer experience for digital platforms could be negatively affected as this change is complex and will require them to perform tasks they do not currently perform. Digital platforms were consulted in the OECD drafting process and HMRC will consult on new regulations in the UK and, in due course, issue clear guidance on how to comply with the new rules.
The government will look to minimise burdens for platforms where possible, while also ensuring that the information reported is accurate and useful. There will also be an optional exemption for start-ups and a phasing in period for some of the obligations to help spread out the initial impact.
Businesses including individuals who sell services or rent out property through Digital Platforms
This measure is expected to have a significant combined impact on an estimated 2-5 million businesses who provide their services via digital platforms though the impact for each seller is expected to be small.
Data, including bank account information if the platform holds that information, will be collected and provided to HMRC, and exchanged with other tax authorities when appropriate. This information will be used to identify and risk assess the individual or company.
One-off costs will include familiarisation with the change and could include providing specific information and documents to digital platforms either when registering or as part of a verification process. This includes name, address, and tax identification number.
There are not expected to be any continuing costs.
Customer experience for these sellers is expected to improve as they will receive a copy of the information that has been submitted to a tax authority. This should help them to declare the right income and may make complying with their tax obligations easier.
HMRC will use findings from their external research programme and from the consultation to estimate the number of businesses who will be affected by this measure more precisely. There is expected to be no impact on civil society organisations.
Impact on HMRC or other public sector delivery organisations
There is an estimated cost to HMRC of £21m including 24 Full Time Equivalent (FTE) required. However, the costs to HMRC are currently being developed further.
Other impacts
A Data Protection Impact Assessment will be undertaken for regulations introduced using this power.
Other impacts have been considered and none has been identified.
The government would welcome views from platform operators and sellers on whether the above impacts on businesses are realistic and accurate. It would also welcome any further details about the impact of collecting, verifying and reporting the required information to HMRC, particularly in terms of the costs that may be incurred, the time taken on additional processes, and the number of platforms and sellers that would be affected.
Source: HM Revenue & Customs
